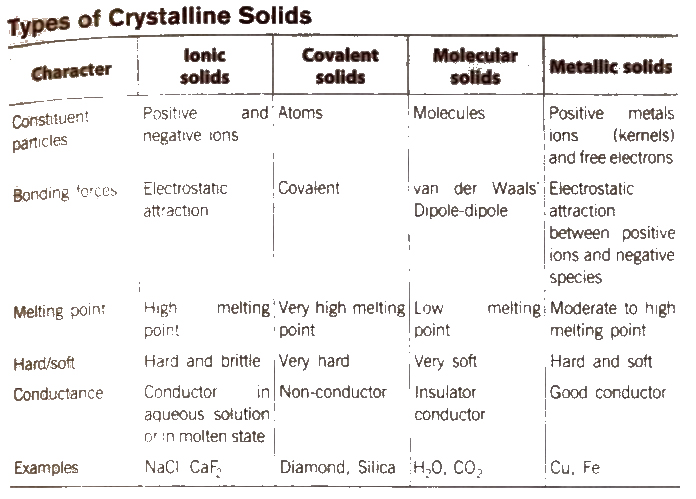
Solids
Solids are the chemical substances which are characterised by define shape and volume, rigidity, high density, low compressibility. The constituent particles (atoms, molecules or ions) are closely packed and held together by strong interparticle forces
Types of Solids
The solids are of two types : Crystalline solids and amorphous solids.
Distinction Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solids
| S.No | Crystalline solid | Amorphous solids |
| 1 | These have definite and regular arrangement of the constituent particles in space. | These doesn’t have any regular arrangement of the constituent particles in space. |
| 2 | These are true solids. | Theseare super cooled liquids or pseudo soilds. |
| 3 | These have long order arrangement of the particles. | These have short order arrangement of particle. |
| 4 | These are anisotropic in nature, i.e., their physical properties are different in different directions. | These are isotropic in nature i.e., their physical properties are same in all the directions. |
| 5 | They have sharp melting points. | They melt over a certain range of temperature. |
| 6 | They undergo a clean cleavage when cut. | They undergo irregular cleavage when cut. |
Structure Determination by X-ray Diffraction (Bragg’s Equation)
When a beam of X-rays falls on a crystal plane composed of regularly arranged atoms or ions, the X-rays are diffracted. If the waves are in phase after reflection, the difference in distance travelled by the two rays ti.e., path difference) must be equal to an integral number of Wavelength, nλ for constructive.
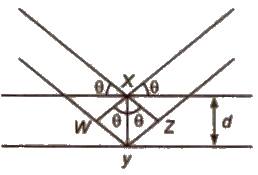
Thus, path difference = WY + YZ
= XY sin θ + xy sin θ
= 2 XY sin θ = 2d sin θ
∴ nλ = 2d sin θ
This equation is called Bragg’s equation.
Where, n = 1. 2, 3… (diffraction order)
λ = wavelength of X·rays incident on crystal
d = distance between atomic planes
θ = angle at which interference occurs.
Unit Cell
The smallest geometrical portion of the crystal lattice which can be used as repetitive unit to build up the whole crystal is called unit cell.
Types of Unit Cell
(i) Simple or primitive Unit cell In which the particles are present at the corners only.

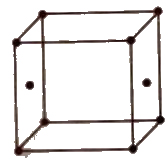
(ii) Face centred unit cell In which the particles are present at the corners as well as at the centre of each of six faces

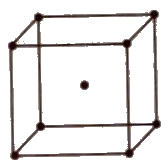
(iii) Body centred unit cell In which the particles are present at the corners as well as at the centre of the unit cell.
(iv) End centred unit cell In which the particles are present at the corners and at the centre of two opposite faces.
Number of Particles Per Unit Cell

Seven Crystal Systems
There are about 230 crystal forms, which have been grouped into 14 types of space lattices, called Bravais Lattices, on the basis of their symmetry and seven different crystal systems on the basis of interfacial angles and axes.
Seven Crystal Systems

Packing Fraction
It is defined as the ratio of the volume of the unit cell that is occupied by the spheres to the volume of the unit cell.
(i) Primitive cubic unit cell Atoms touch each other along edges.
Hence, d = a or r = a / 2
(r = radius of atom and a = edge length)
Therefore, PF = 4 / 3 πr3 / (2r)3 = 0.524 or 52.4%
(ii) Face centred cubic unit cell Atoms touch each other along the face diagonal.
Hence, d = a / √2
or r = √2a / 4
Therefore; PF = 4 * 4 / 3 πr3 / (4r / √2)r3 = 0.74 or 74%
(iii) Body centred cubic unit cell Atoms touch each other along the body diagonal.
Hence, √3a / 2
or r = √3a / 4
Therefore; PF = 2 * 4 / 3 πr3 / (4r / √3)r3 = 0.68 or 68%
Coordination Number
It is defined as the number of particles immediately adjacent to each particle in the crystal lattice.
[In simple cubic lattice, CN is 6, in body centred lattice, CN is 8 and in face centred cubic lattice, CN is 12].
High pressure increases CN and high temperature decreases the CN.
Close Packing in Crystals
Two Dimensional Packing of Constituent Particles
(i) Square close packing Space occupied by spheres is 52.4%.

(ii) Hexagonal close packing Space occupied by spheres is 60.4%.Hence. It is more efficient.

Three Dimensional Packing of Constituent Particles
(i) ABAB arrangement gives hexagonal close packing (hcp).
(ii) ABCABC arrangement gives cubic close packing or face centred CUbIC packing (ccp or fcc).
- In both these arrangements 740/0 space is occupied
- Coordination number in hop and ccp arrangement is 12 while in bcc arrangement, it is 8.
- Close packing of atoms in cubic structure = fcc > bcc > sc.
- All noble gases have ccp structure except He (hcp structure).
Void or Space or Holes
- Empty or vacant space present bet veen spheres of a unit cell, is called void or space or hole or interstitial void. When particles are closed packed resulting in either cpp or hcp structure, two types of voids are generated:
- Tetrahedral voids are holes or voids surrounded by four spheres Present at the corner of a tetrahedron. Coordination number of a tetrahedral void is 4.

- Octahedral voids are holes surrounded by six spheres located on a regular tetrahedron. Coordination number of octahedral void is 6.

[The number of octahedral voids present in a lattice is equal to the number of close packed particles. The number of tetrahedral voids present in a lattice is twice to the number of close packed particles.]
Density of Unit Cell (d)
Density of unit ce11 = mass of unit cell / volume of unit cell
d = Z * M / a3 = ZM / a3 * NA
(The density of the unit cell is same as the density of the substance.)
where, d = density of unit cell
M = molecular weight
Z = no. of atoms per unit cell
NA = Avogadro number
a = edge length of unit cell.
The Structure of Ionic Crystals
The ionic radius ratios of cation and anion, play a very important role in giving a clue to the nature of the crystal structure of ionic substances.
Radius Ratio and Crystal Structure

Ionic crystals may be of two types
(i)AB type and
(ii) A2B or AB2
Structure of Ionic Crystals
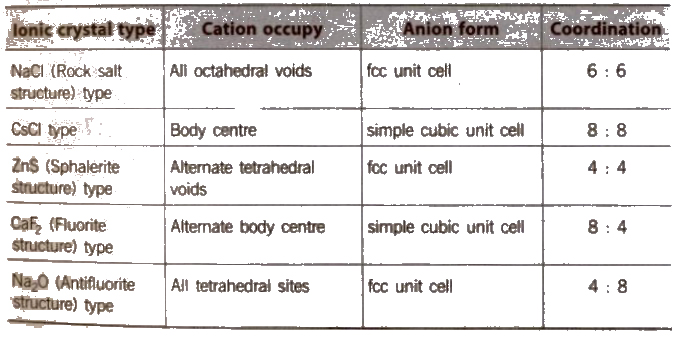
On applying pressure NaC} structure (6 : 6 coordination) changes into CsCI structure (8 : 8 coordination) and reverse of this occur at high temperature (760 K).
Imperfections in Solids
- In a crystalline solid, the atoms, ions and molecules are arranged in a Definite repeating pattern, but some defects may occur in the pattern. derivations from perfect arrangement may occur due to rapid cooling or presence of additional particles.
- The defects are of two types, namely point defects and line defects.
Point Defects
Point defects are the irregularities or deviations from ideal arrangement around a point or an atom in a crystalline substance Point defects can be classified into three types : (1) psychometric defects (2) impurity defects (3) non–stoichiometric defects
1. Stoichiometric Defect
These are point defects that do not disturb’ the -stoichiometric of the solid. They are also called intrinsic or thermodynamic defects. In ionic solids, basically these are of two types, Frankel defect and Schottky defect

AgBr has both Schottky and Frenkel defects. Frenkel defects are not found in pure alkali metal halides because cations are of large size.
2. Impurity Defect
- It arises when foreign atoms or ions aloe present in the lattice. In case of ionic compounds, the impurity 1S also ionic in nature. When the impurity has the same charge as the host ion. it just substitutes some of the host ions.
- Impurity defects can also be introduced by adding impurity ions having different charge than host ions. e.g. molten NaCl containing a little amount of SrCI2 is crystallised. In such cases,
- Cationic vacancies produced = [number of cations of higher valence * Difference in valence of the host cation and cation of higher valence
3. Non-Stoichiometric Defect
Non-stoichiometric crystals are those which do not obey the law of constant proportions. The numbers of positive and negative ions present in such compounds are different from those expected from their ideal chemical formulae. However, the crystal as a whole in neutral.
Types of n-stoichiometric defects are as follows:
(i) Met excess defect Metal excess defect due to anionic vacancies: Alkyl halides like NaC1 and KCl show this type of defect. centres ale the sites from where anions are missing and the vacant sites are occupied by electrons. F-centres contribute colour and paramagnetic nature of the crystal [F stands for
German wo\d Farbe meaning colour).
Metal excess defect due to presence of extra cations at interstitial sites, e.g., zinc oxide is white in colour at room temperature. On beating, it loses oxygen and turns yellow.
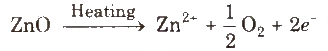
(ii) Metal deficiency defect due to cation vacancy It is due to the absence of a metal ion from its lattice site and charge is balanced by ion having higher positive charge. Transition metals exhibit this defect, e.g., FeO, which is found in the composition range from Fe0.93 O to Fe0.96O.
In crystal of FeO, some Fe2+cations are missing and the loss of positive charge is made up by the presence of required number of Fe3+ ions.
Classification of Solids on the Basis of Electrical Conductivity

[The electricity produced on heating a polar crystal is called ‘pyroelectricity’.]
When mechanical stress is applied on polar crystals, electricity produced due to displacement of ions is called ‘piezoelectricity’
Semiconductors
Electronic conductors having electrical conductivity in the range of 104 – 107 Ω-1 cm-1are known as semiconductors. Examples Si, Ge Sn (grey), Cu2O, SiC and GaAs.
Intrinsic Semiconductors
Pure substances that are semiconductors are known as Intrinsic Semiconductors e.g., Si, Ge
Extrinsic Semiconductors
Their conductivity is due to the presence of impurities. They are formed by doping. It is defined as addition of impurities to a semiconductor to increase the conductivity. Doping of Si or Ge is carried out with P, As, Sb, B, Al or Ga.
(i) n·type semiconductors Silicon doped with 15 group elements like phosphorus is called n-type semiconductor. The conductivity is due to the presence of negative charge (electrons),
(ii) p·type semiconductors Silicon doped with 13 group element like gallium is called p-type semiconductor. The conductivity is due to the presence of positive holes.
- Some typical 13-15 compounds are InSb, AlP and GaAs and SOme typical 12-16 compounds are ZnS, CdS. CdSe and HgTe.
- These exhibit electrical and optical properties of great use in electronic industry.
Magnetic Properties of Solids
Solids can be divided into different classes depending on their response to magnetic field.
1. Diamagnetic Substances
These are weakly repelled by the magnetic field and do not have any unpaired electron, e.g., TiO2, V2O5, C6H6, NaCI, etc.
2. Paramagnetic Substances
These are attracted by the magnetic field and have unpaired electrons These lose magnetism in the absence of magnetic field, e.g., O2, Cu2+, Fe3+, etc.
3. Ferromagnetic Substances
These are attracted by the magnetic field and show permanent magnetism even ill the absence of magnetic field e.g., Fe, Co and Ni.
4. Anti-ferromagnetic Substances
These substances have net magnetic moment zero due to compensatory alignment of magnetic . moments, e.g., MnO, MnO2, FeO, etc.
5. Ferrimagnetic Substances
These substances have a net dipole moment due to unequal parallel and anti-parallel alignment of magnetic moments, e.g., Fe3O4, ferrites, etc.






COMMENTS